graphql-authorization.md 1.5 KB
GraphQL 鉴权
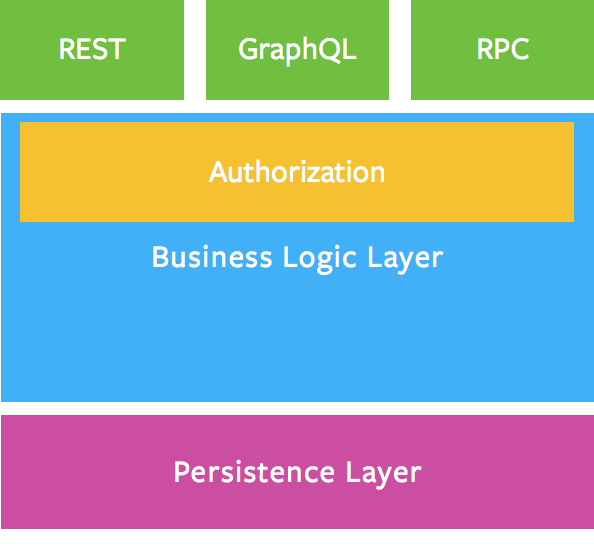
GraphQL项目的架构:
其中鉴权部分应当属于业务逻辑层.
注意事项
这里是一个鉴权的例子, 作者可以管理(编辑)自己的文章, 在定义模型的时候加入了权限的判断:
var postType = new GraphQLObjectType({
name: ‘Post’,
fields: {
body: {
type: GraphQLString,
resolve: (post, args, context, { rootValue }) => {
// return the post body only if the user is the post's author
if (context.user && (context.user.id === post.authorId)) {
return post.body;
}
return null;
}
}
}
});
但有个问题在于, 鉴权的逻辑不被保留完全同步, 用户通过其他方式调用(如通过RESTful接口)时依然需要重新鉴权.
//Authorization logic lives inside postRepository
var postRepository = require('postRepository');
var postType = new GraphQLObjectType({
name: ‘Post’,
fields: {
body: {
type: GraphQLString,
resolve: (post, args, context, { rootValue }) => {
return postRepository.getBody(context.user, post);
}
}
}
});
这样, 我们就可以将用户对象传递到下一层(业务逻辑层)去进行鉴权的处理.
鉴权中间件
Express中的GraphQL鉴权中间件示例: https://graphql.js.cool/graphql-js/authentication-and-express-middleware/
示例项目
完整示例项目待添加.